김영한(인프런 강의)/자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래밍
연관관계 매핑 기초 - 단방향 연관관계
레알윙
2020. 10. 7. 13:19
반응형
연관관계를 왜 만드는가?
객체지향 설계의 목표는 자율적인 객체들의 협력 공동체를 만드는 것이다.
– 조영호(객체지향의 사실과 오해)
예상 시나리오
1) 회원과 팀이 있다.
2) 회원은 하나의 팀에만 소속될 수 있다.
3) 회원과 팀은 다대일 관계다.
연관관계 없는 객체 모델링
1. 연관관계(연관관계 없음)
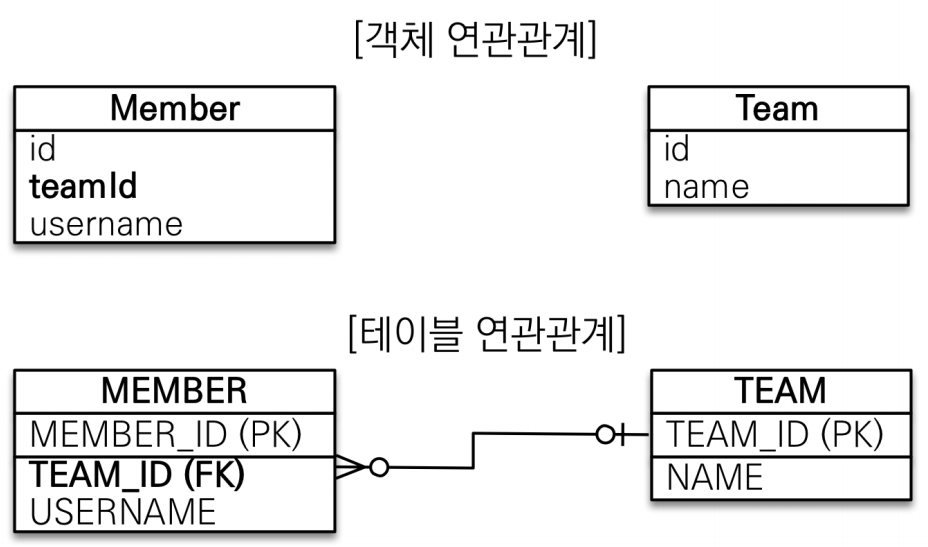
2. 특징
1) 객체를 테이블에 맞추어 모델링을 해야 한다.
- 참조 대신에 외래 키를 그대로 사용
@Entity
public class Member {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column(name = "USERNAME")
private String name;
@Column(name = "TEAM_ID")
private Long teamId;
Getter(), Setter() ...
}
@Entity
public class Team {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
Getter(), Setter() ...
}- 외래 키 식별자를 직접 다룸
public class JpaStudyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction tx = em.getTransaction();
// 트랜잭션 시작
tx.begin();
try {
// 팀 저장
Team team = new Team();
team.setName("TeamA");
em.persist(team);
// 회원 저장
Member member = new Member();
member.setName("member1");
member.setTeamId(team.getId());
em.persist(member);
tx.commit(); // [트랜잭션] 커밋
} catch (Exception e) {
tx.rollback();
} finally {
em.close();
}
emf.close();
}
}- 식별자로 다시 조회, 객체 지향적인 방법은 아니다.
public class JpaStudyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction tx = em.getTransaction();
//트랜잭션 시작
tx.begin();
try {
//조회
Member findMember = em.find(Member.class, member.getId());
//연관관계가 없음
Team findTeam = em.find(Team.class, team.getId());
tx.commit(); // [트랜잭션] 커밋
}catch (Exception e) {
tx.rollback();
}finally {
em.close();
}
emf.close();
}
}2) 객체를 테이블에 맞추어 데이터 중심으로 모델링하면, 협력 관계를 만들 수 없다.
- 테이블은 외래 키로 조인을 사용해서 연관된 테이블을 찾는다
- 객체는 참조를 사용해서 연관된 객체를 찾는다.
- 테이블과 객체 사이에는 위의 코드로 설명한 것처럼 큰 간격이 있다.
단방향 연관관계
1. 연관관계(객체 연관관계 사용)

2. 특징
1) 객체를 테이블에 맞추어 모델링
- 객체의 참조와 테이블의 외래 키를 매핑
@Entity
public class Member {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column(name = "USERNAME")
private String name;
private int age;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "TEAM_ID")
private Team team;
Getter(). Setter() ...
}
@Entity
public class Team {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "TEAM_ID")
private Long id;
private String name;
Getter(), Setter()
}- 연관관계 저장
public class JpaStudyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction tx = em.getTransaction();
// 트랜잭션 시작
tx.begin();
try {
// 팀 저장
Team team = new Team();
team.setName("TeamA");
em.persist(team);
// 회원 저장
Member member = new Member();
member.setName("member1");
member.setTeam(team); // 단방향 연관관계 설정, 참조 저장
em.persist(member);
tx.commit(); // [트랜잭션] 커밋
} catch (Exception e) {
tx.rollback();
} finally {
em.close();
}
emf.close();
}
}- 참조로 연관관계 조회 - 객체 그래프 탐색
public class JpaStudyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction tx = em.getTransaction();
// 트랜잭션 시작
tx.begin();
try {
// 조회
Member findMember = em.find(Member.class, member.getId());
// 참조를 사용해서 연관관계 조회
Team findTeam = findMember.getTeam();
tx.commit(); // [트랜잭션] 커밋
} catch (Exception e) {
tx.rollback();
} finally {
em.close();
}
emf.close();
}
}- 연관관계 수정
public class JpaStudyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction tx = em.getTransaction();
// 트랜잭션 시작
tx.begin();
try {
// 새로운 팀B
Team teamB = new Team();
teamB.setName("TeamB");
em.persist(teamB);
// 회원1에 새로운 팀B 설정
member.setTeam(teamB);
tx.commit(); // [트랜잭션] 커밋
} catch (Exception e) {
tx.rollback();
} finally {
em.close();
}
emf.close();
}
}
반응형